What is 1.1.1.1?
1.1.1.1 is a fast and private way to browse the Internet. It is a public DNS resolver,
but unlike most DNS resolvers, 1.1.1.1 is not selling user data to
advertisers. The implementation of 1.1.1.1 makes it the fastest resolver
out there.
What is DNS?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the phonebook of the Internet. Humans access information online
through domain names, like nytimes.com or espn.com. Web browsers
interact through Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. DNS translates domain
names to IP addresses so browsers can load Internet resources.
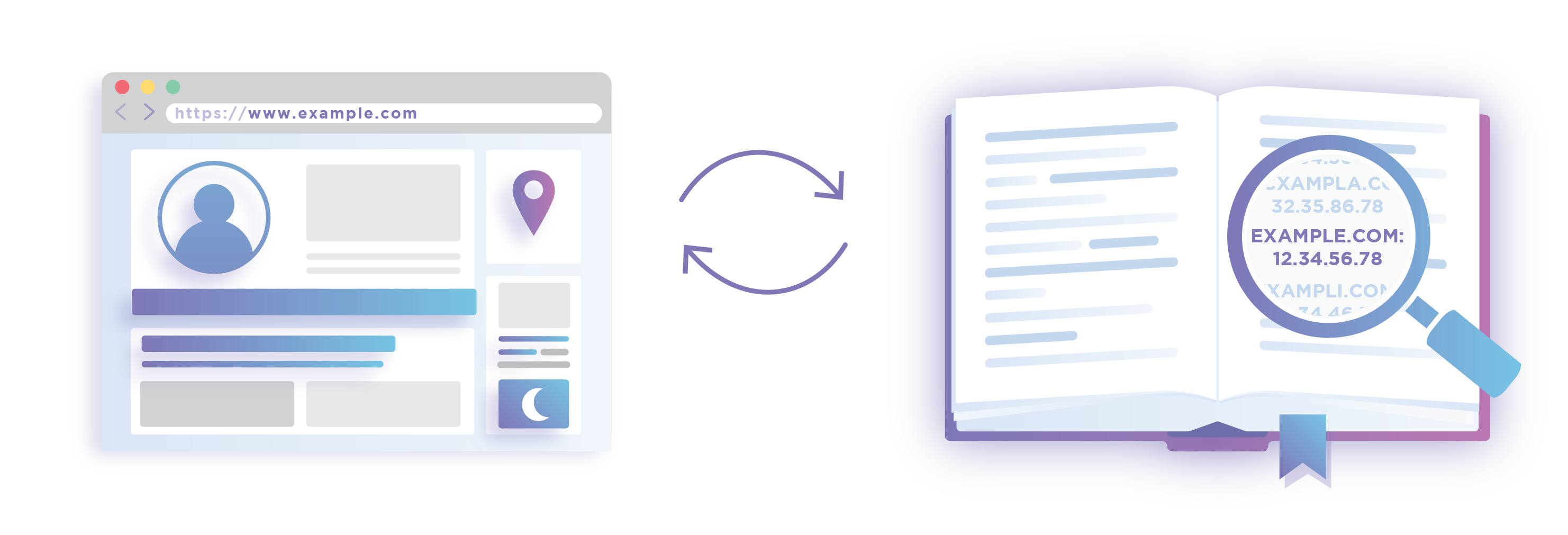
Each device connected to the Internet has a unique IP address which other machines use to find the device. DNS servers eliminate the
need for humans to memorize IP addresses such as 192.168.1.1 (in IPv4),
or more complex newer alphanumeric IP addresses such as
2400:cb00:2048:1::c629:d7a2 (in IPv6).
What is a DNS resolver?
When a user requests to visit a web application like
facebook.com, the user’s computer needs to know what server to connect
to so that it can load the application. Computers don’t initially have
the necessary information to do this ''name to address'' translation, so
they ask a specialized server to do it for them.
This specialized server is called a DNS recursive
resolver. The resolver’s job is to find the address for a given name,
like 2400:cb00:2048:1::c629:d7a2 for cloudflare.com, and return it to
the computer that asked for it.
Computers are configured to talk to specific DNS
resolvers, identified by IP address. Usually the configuration is
managed by the user’s ISP (like Comcast or AT&T) on home or wireless
connections, and by an network administrator on office connections.
Users can also manually change which DNS resolver their computers talk
to.
Why use 1.1.1.1 instead of an ISP’s resolver?
The main reasons to switch to a third-party DNS resolver
are security and performance. ISPs do not always use strong encryption
on their DNS or support DNSSEC, which makes their DNS queries vulnerable to data breaches and exposes users to threats like man-in-the-middle attacks.
In addition, ISPs often use DNS records to track their users’ activity
and behavior. These resolvers don’t always have great speeds and when
they get overloaded by heavy usage they become even more sluggish. If
there is enough traffic on the network, an ISP’s recursor could stop
answering requests altogether. In some cases attackers deliberately
overload an ISP’s recursors, resulting in a denial-of-service.

These downsides and risks of ISP recursors can be
mitigated with a secure recursive DNS service like 1.1.1.1. With
security features like bleeding-edge encryption and the fastest
resolution speeds, 1.1.1.1 provides a better overall user experience.
What makes 1.1.1.1 more secure than other public DNS services?
Some other recursive DNS services may claim that their
services are secure because they support DNSSEC. While this is a good
security practice, users of these services are ironically not protected
from the DNS companies themselves. Many of these companies collect data
from their DNS customers to use for commercial purposes. Alternatively,
1.1.1.1 does not mine any user data. Logs are kept for 24 hours for
debugging purposes, then they are purged.
1.1.1.1 also offers some security features not available
from many other public DNS services, such as query name minimization.
Query name minimization diminishes privacy leakage by only sending
minimal query names to authoritative DNS servers.
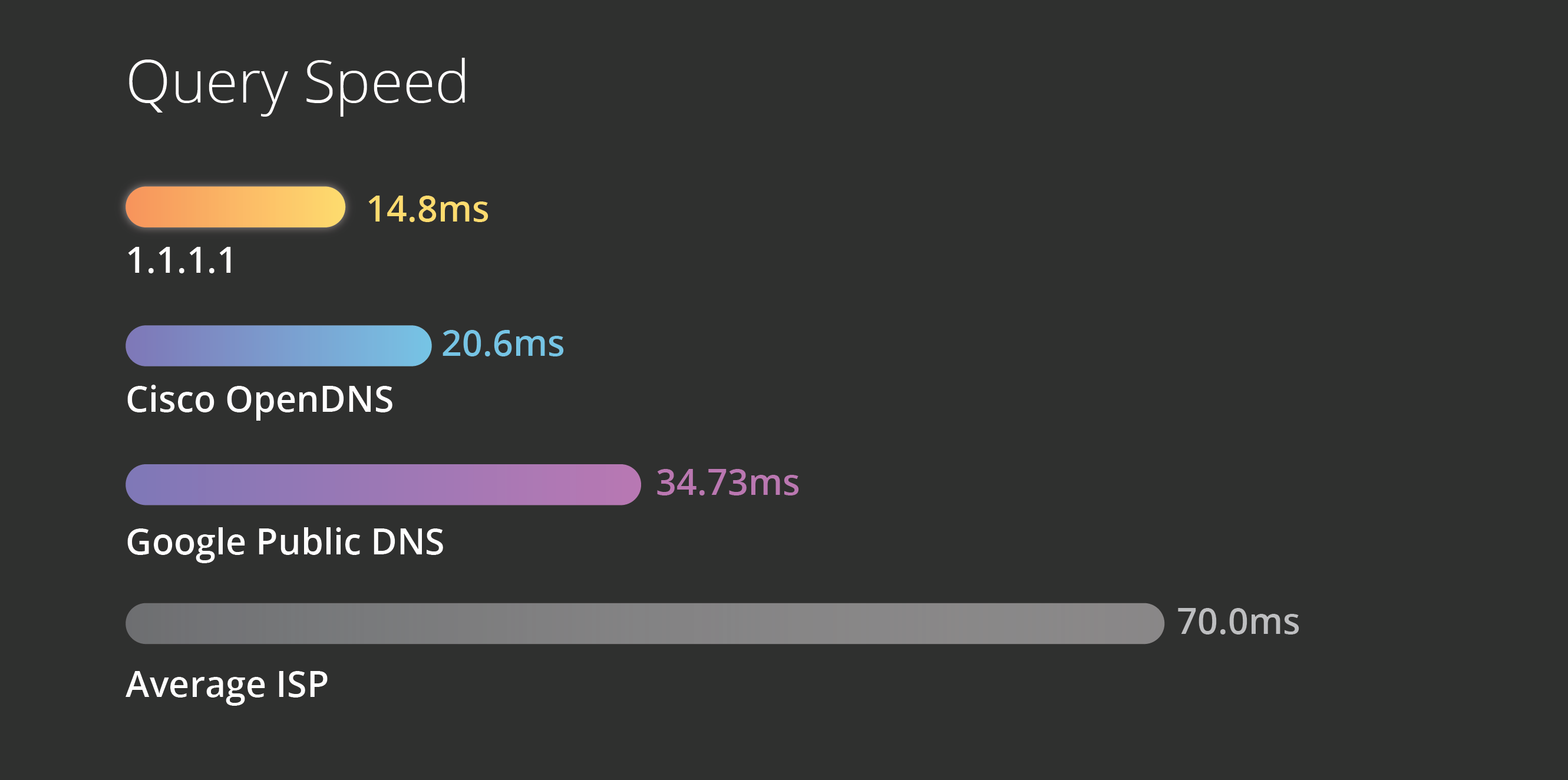
What makes 1.1.1.1 the fastest recursive DNS service?
The power of the Cloudflare network makes gives 1.1.1.1 a
natural advantage in terms of delivering speedy DNS queries. Since it
has been deployed on Cloudflare’s 1000+ servers worldwide, users
anywhere in the world will get a quick response from 1.1.1.1; in
addition to this, these servers have access to the over 7 million
domains on the Cloudflare platform, making queries for those domains
lightning-fast.